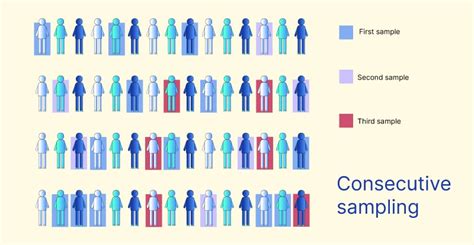
consecutive sampling in quantitative research|consecutive sampling vs convenience sampling : manufacturers Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs .
web0. Em Minecraft. os gamers que escolhem o modo Sobrevivência precisam estar bem. preparados para enfrentar os perigos. Neste tutorial você aprenderá a. usar o .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Locais Cidade - Portilho Online – Sem Censura ! – Noticias d.
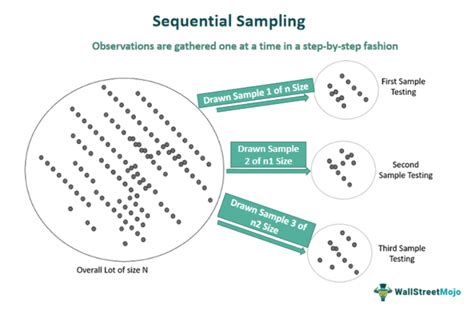
what is sequential sampling
Convenience sampling: the participants are consecutively selected in order of apperance according to their convenient accessibility (also known as consecutive sampling). The .Consecutive sampling is defined as a nonprobability technique where samples are picked at the ease of a researcher more like convenience sampling, only with a slight variation. Here, the .
SKZ1062C Dry and wet method laser particle size Analyzer distribute
This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. In .In the design of experiments, consecutive sampling, also known as total enumerative sampling, [1] is a sampling technique in which every subject meeting the criteria of inclusion is selected . In clinical settings, consecutive sampling provides insight into the number of eligible patients (allowing the calculation of a response rate) and enables the use of clinical .
Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs .Consecutive sampling is the process of doing research with the sample members that meet the inclusion criteria and are conveniently available. You conduct research one after the other until you reach a conclusive result.
Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and . Example: Sampling frame You are doing research on working conditions at a social media marketing company. Your population is all 1000 employees of the company. . It is mainly used in quantitative research. If . River sampling. You are part of a research group investigating online behavior and cyberbullying, in particular among users aged 15 to 30 in your state. You are collecting data in two ways, using an online survey. . These are used in both quantitative and qualitative research. Advantages and disadvantages of non-probability sampling.
Sampling methods: quantitative research. Probability (representative) sampling includes techniques used to select a sample that clearly represents a specific population. Participants are randomly selected so that all members of .In the design of experiments, consecutive sampling, also known as total enumerative sampling, [1] is a sampling technique in which every subject meeting the criteria of inclusion is selected until the required sample size is achieved. [2] Along with convenience sampling and snowball sampling, consecutive sampling is one of the most commonly used kinds of nonprobability .Convenience sampling also has two subtypes: Consecutive sampling (also known as total enumerative sampling) Consecutive sampling is the process of doing research with the sample members that meet the inclusion criteria and are conveniently available. You conduct market research one after the other until you reach a conclusive result. Samples .Reports can be generated based on the combination of data sets (like user profiles, statistics, market research, analytics data) regarding your interactions and those of other users with advertising or (non-advertising) content to identify common characteristics (for instance, to determine which target audiences are more receptive to an ad .
Editor's note: This is the third article in a series on clinical research by nurses. The series is designed to give nurses the knowledge and skills they need to participate in research, step by step. . Sampling Design in Nursing Research Am J Nurs. 2021 Mar 1;121(3):53-57. doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000737304.14564.51. Authors Alexa Colgrove Curtis .Convenience sampling also has two subtypes: Consecutive sampling (also known as total enumerative sampling) Consecutive sampling is the process of doing research with the sample members that meet the inclusion criteria and are conveniently available. You conduct research one after the other until you reach a conclusive result. Samples are .Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for c .The sampling process (25 minute read time); Sampling approaches for quantitative research (15 minute read time); Sample quality (24 minute read time); Content warning: examples contain references to addiction to technology, domestic violence and batterer intervention, cancer, illegal drug use, LGBTQ+ discrimination, binge drinking, intimate partner violence among college .
Sampel dalam penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas II SLBN 1 Kota Jambi, yang terdiri dari 1 siswa laki-laki dan 2 siswa perempuan. Metode pemilihan sampel yang digunakan adalah purposive sampling, di . There are two different types of sampling methods for quantitative research and they are: 1. Probability Sampling. . Consecutive Sampling: It is very much similar to convenience sampling, except the researchers can select a group or a single element of the samples. This method conducts the research consecutively over an important period and . When to use purposive sampling. Purposive sampling is best used when you want to focus in depth on relatively small samples.Perhaps you would like to access a particular subset of the population that shares certain characteristics, or you are researching issues likely to have unique cases.. The main goal of purposive sampling is to identify the cases, individuals, .
Convenience sampling is a type of sampling where the first available primary data source will be used for the research without additional requirements. In other words, this sampling method involves getting participants wherever you can find them and typically wherever is convenient.-Used for research such as large-scale surveys-Successive random sampling of units—multistage sampling (e.g. states, census tracts, then households)-Less accurate than simple random or stratified random sampling, but more economical and practicalAns: A Feedback: Convenience sampling is used by both quantitative and qualitative researchers, but it is not the preferred approach by either group. Both quantitative and qualitative researchers identify eligibility criteria for their studies, and both are concerned about the quality of their samples (although they use different criteria for deciding what a "good" sample is). 30. Consecutive sampling • Also known as Total enumerative sampling. • It includes all the subjects that meet the inclusion criteria. e.g post kidney transplant patients. • The researcher conduct research one after the .
The sampling technique in this study was a consecutive sampling technique in which the researcher used the entire population for the sample (Bjørn et al., 1998; Martínez-Mesa et al., 2016). The . ful, and quota sampling. In quantitative research, proba- . Consecutive sampling is one method of purposeful. . it is a prevalent sampling technique in qualitative research, wherein the .The result of sampling is thus more likely to represent the target population that the resulting of convenience sampling. consecutive sampling is more reliable than convenient. see the following .Convenience sampling is a type of non-probability sampling method in research where the sample is drawn from the part of the population that is readily available and easiest for the researcher to access. . it can be used in both qualitative and quantitative research, though it's most often used in quantitative studies as a non-random sampling .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like ____ is the process of selecting a portion of the population, which is an entire aggregate of cases. An element is the basic population unit about which information is collected—usually humans in nursing research., Sampling is the process of selecting a portion of the ____, which is an entire aggregate of . The data collected is quantitative and statistical analyses are used to draw conclusions. Purpose of Sampling Methods. The main purpose of sampling methods in research is to obtain a representative sample of individuals or elements from a larger population of interest, in order to make inferences about the population as a whole.
In this section, let’s explore four standard sampling techniques in qualitative research: purposive sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling, and theoretical sampling. We’ll break down the definition of each technique, when to use it, and its advantages and disadvantages. . We also offer qualitative and quantitative research . The sampling technique in quantitative research comes from its ability to draw small units of the population (i.e., sample size) and generalize it to the population (Seddon & Scheepers, 2012).In a study, specifically in behavioural research where the number of population elements is too large, collecting data from every element of a population is unreal.
The convenience sampling technique was used in this research. Convenience sampling is one of the non-probability sampling techniques and a way of selecting participants from the target population . Quantitative research is a method that uses numbers and statistics to gather precise, measurable data on the research subject. Offering numbers and stats-based insights, this research methodology is a crucial part of primary research and helps understand how well an organizational decision will work out.
consecutive vs convenience sampling
consecutive sampling vs purposive sampling
Dry and wet method laser particle size Analyzer distribute
consecutive sampling vs purposive
Resultado da 12 de mar. de 2021 · Acesse o aplicativo Caixa TEM no seu celular, usando seu login e senha. Clique em "atualizar seu cadastro" Envie a .
consecutive sampling in quantitative research|consecutive sampling vs convenience sampling